
最近在做项目技术栈整理工作;
由于团队越来越大、人员增多、项目增多;
统一技术栈是一件非常有必要的事;

React 状态管理工具有很多,但是选择一个合适的状态管理工具其实很重要;
今天跟大家分享一下我整理的几个非常热门的 React状态管理,希望对你有所帮助。
【 1. Mobx 】

Mobx
MobX 可以独立于 React 运行, 但是他们通常是结合在一起使用;新版的 mobx-react-lite 库非常轻量;使用时只需要使用导出的observer包裹组件; 然后引入状态即可;
import React from "react"
import ReactDOM from "react-dom"
import { makeAutoObservable } from "mobx"
import { observer } from "mobx-react-lite"
class Timer {
secondsPassed = 0
constructor() {
makeAutoObservable(this)
}
increaseTimer() {
this.secondsPassed += 1
}
}
const myTimer = new Timer()
//被`observer`包裹的函数式组件会被监听在它每一次调用前发生的任何变化
const TimerView = observer(({ timer }) =>
<span>Seconds passed: {timer.secondsPassed}
</span>)
ReactDOM.render(<TimerView timer={myTimer} />, document.body)【 2. Redux 】
Redux
Redux 也是一个非常流行的状态管理,只不过比起其他的状态管理工具,会显得笨重一些;当然喜欢使用Redux的人也会觉得Redux 非常的优雅;
import { createStore } from 'redux'
/**
* This is a reducer - a function that takes a current state value and an
* action object describing "what happened", and returns a new state value.
* A reducer's function signature is: (state, action) => newState
*
* The Redux state should contain only plain JS objects, arrays, and primitives.
* The root state value is usually an object. It's important that you should
* not mutate the state object, but return a new object if the state changes.
*
* You can use any conditional logic you want in a reducer. In this example,
* we use a switch statement, but it's not required.
*/
function counterReducer(state = { value: 0 }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'counter/incremented':
return { value: state.value + 1 }
case 'counter/decremented':
return { value: state.value - 1 }
default:
return state
}
}
// Create a Redux store holding the state of your app.
// Its API is { subscribe, dispatch, getState }.
let store = createStore(counterReducer)
// You can use subscribe() to update the UI in response to state changes.
// Normally you'd use a view binding library (e.g. React Redux) rather than subscribe() directly.
// There may be additional use cases where it's helpful to subscribe as well.
store.subscribe(() => console.log(store.getState()))
// The only way to mutate the internal state is to dispatch an action.
// The actions can be serialized, logged or stored and later replayed.
store.dispatch({ type: 'counter/incremented' })
// {value: 1}
store.dispatch({ type: 'counter/incremented' })
// {value: 2}
store.dispatch({ type: 'counter/decremented' })
// {value: 1}想要很快上手Redux 不是一件容易的事,还需要仔细琢磨一下; 不过好在redux官方推出了新的Redux-tookit 大大简化了使用Redux的步骤。
【 3. Rematch 】
Rematch
Rematch 延续了Redux的优点,核心概念还是基于Redux;但是比起Redux,它简直太强大了!。
import { createModel } from "@rematch/core";
import { RootModel } from ".";
export const count = createModel<RootModel>()({
state: 0, // initial state
reducers: {
// handle state changes with pure functions
increment(state, payload: number) {
return state + payload;
},
},
effects: (dispatch) => ({
// handle state changes with impure functions.
// use async/await for async actions
async incrementAsync(payload: number, state) {
console.log("This is current root state", state);
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
dispatch.count.increment(payload);
},
}),
});以下是Rematch 的一些特性:
- 小于2kb的大小
- 不需要配置
- 减少Redux样板文件
- 内置副作用支持
- React Devtools支持
- TypeScript 原生支持
- 支持动态添加reducers
- 支持热重载
- 允许创建多个store
- 支持React Native
- 可扩展的插件
Rematch 的store还是延续了一些Redux的写法,只不过总体是精简了许多。想要上手也是非常轻松的。
【 4. Recoil 】
Recoil
Recoil 提供了一种新的状态管理模型——Atom模型,它可以更好地处理复杂的状态逻辑。
如需在组件中使用 Recoil,则可以将 RecoilRoot 放置在父组件的某个位置。将他设为根组件为最佳:
import React from 'react';
import {
RecoilRoot,
atom,
selector,
useRecoilState,
useRecoilValue,
} from 'recoil';
function App() {
return (
<RecoilRoot>
<CharacterCounter />
</RecoilRoot>
);
}一个 atom 代表一个状态。Atom 可在任意组件中进行读写。读取 atom 值的组件隐式订阅了该 atom,因此任何 atom 的更新都将致使使用对应 atom 的组件重新渲染;
使用atom状态,需要在组件内引入 useRecoilState:
const textState = atom({
key: 'textState', // unique ID (with respect to other atoms/selectors)
default: '', // default value (aka initial value)
});
function CharacterCounter() {
return (
<div>
<TextInput />
<CharacterCount />
</div>
);
}
function TextInput() {
const [text, setText] = useRecoilState(textState);
const onChange = (event) => {
setText(event.target.value);
};
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={text} onChange={onChange} />
<br />
Echo: {text}
</div>
);
}【 5. Hookstate 】

hookState
HookState 也是一个非常简单的状态管理工具库,它直观的Api,供你轻松的访问状态;
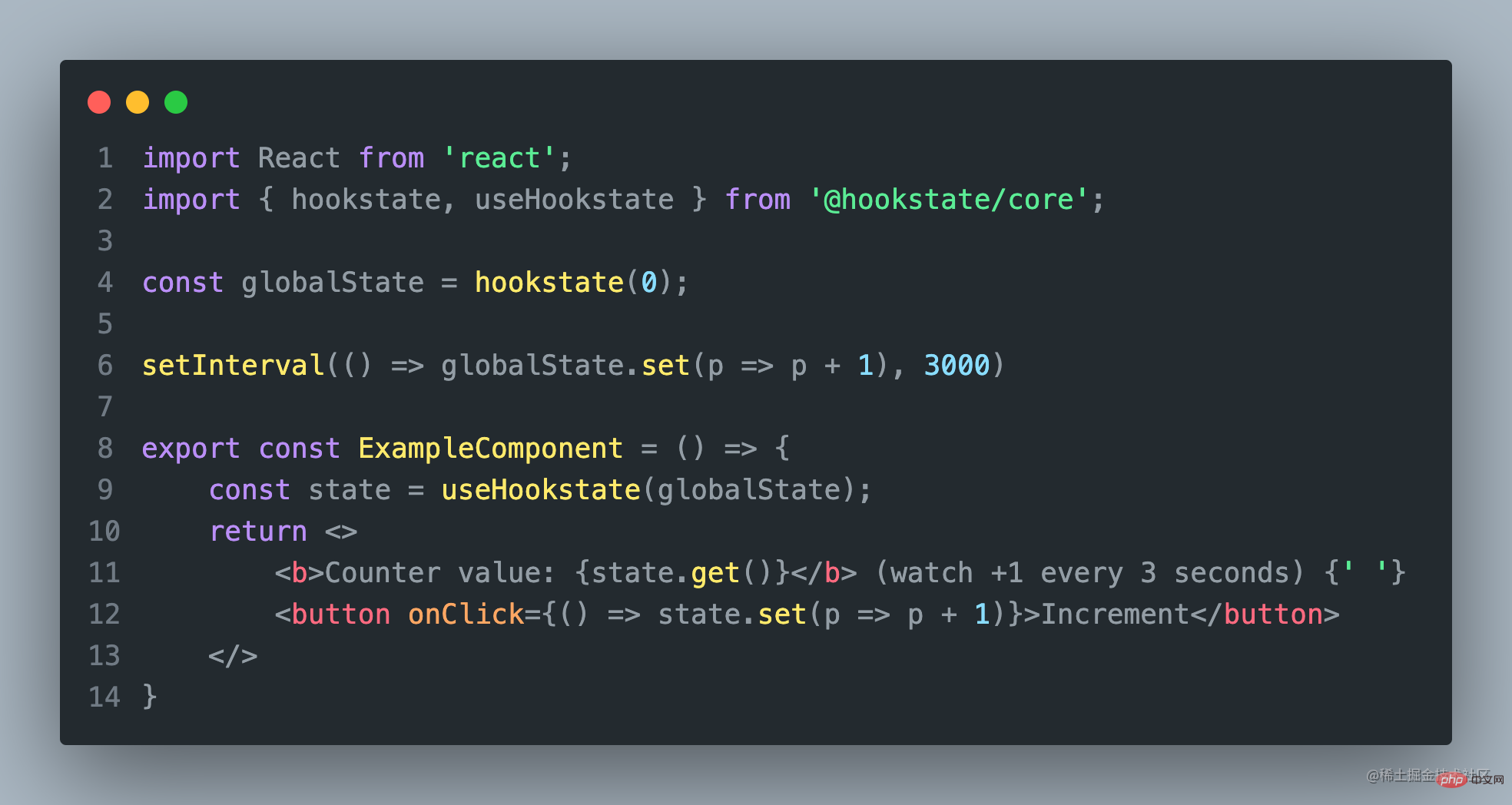
它的主要特点包括:
HookState 主要包括两个重要的Api HookState、useHookState。
如果还需要其他功能,可以参考官方提供的其他更多Api。
【 6. Jotai 】
Jotai
Jotai 是一个 React 的原始和灵活的状态管理库。它类似于 Recoil,但具有更小的包大小 、更简约的 API、更好的 TypeScript 支持、更广泛的文档以及没有实验性标签。
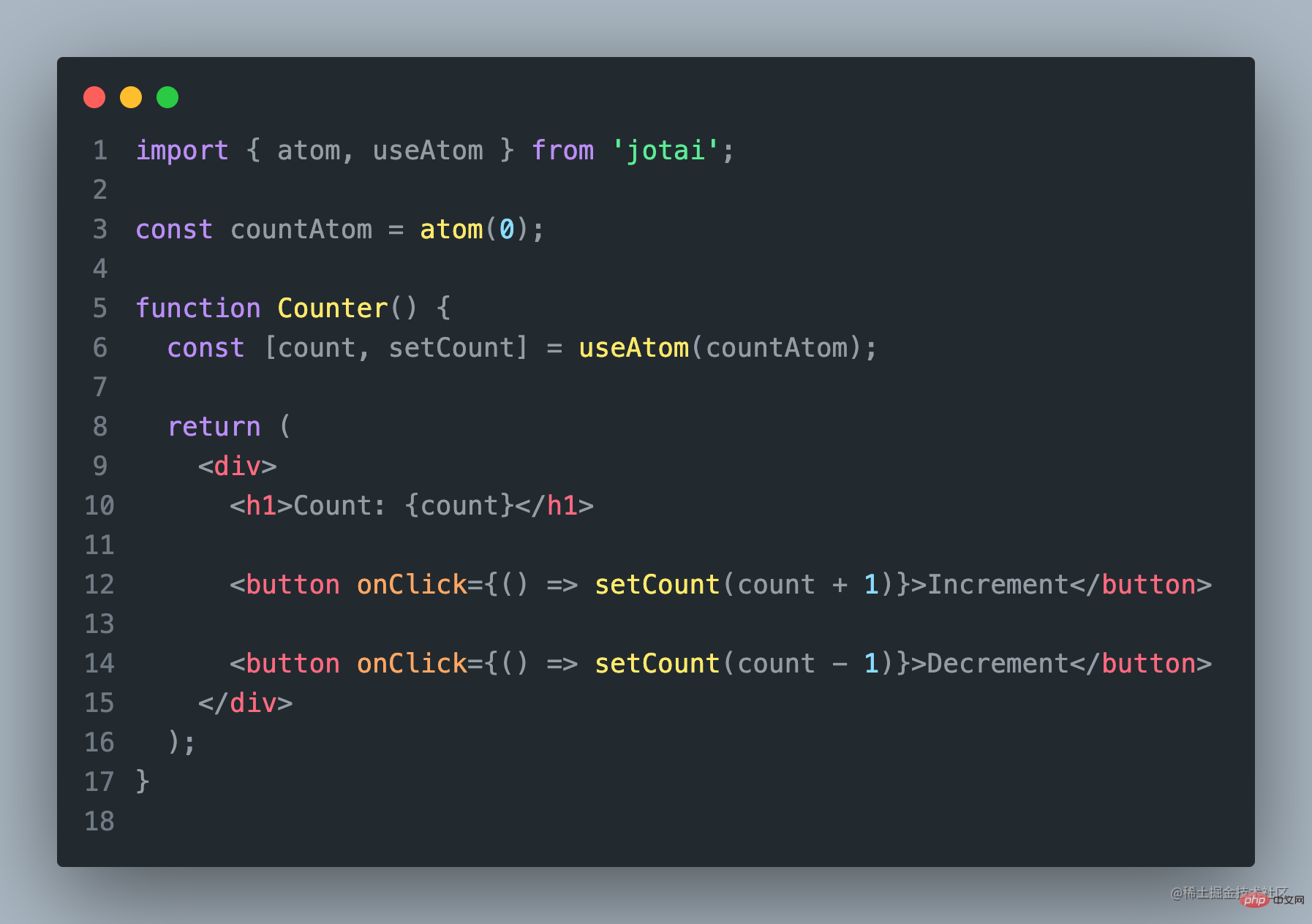
使用Jotai,你可以将状态存储在一个单一的store中,并使用自定义的hooks来访问和更新状态。
import { atom, useAtom } from 'jotai';
const countAtom = atom(0);
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useAtom(countAtom);
return (
<div>
<h1>Count: {count}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increment</button>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count - 1)}>Decrement</button>
</div>
);
}以上是Jotai的使用示例代码,使用Jotai非常简单。
【 7. Zustand】

Zustand 提供了一种简单的方式来管理React应用程序中的状态。
它的主要特点是易于使用和轻量级。
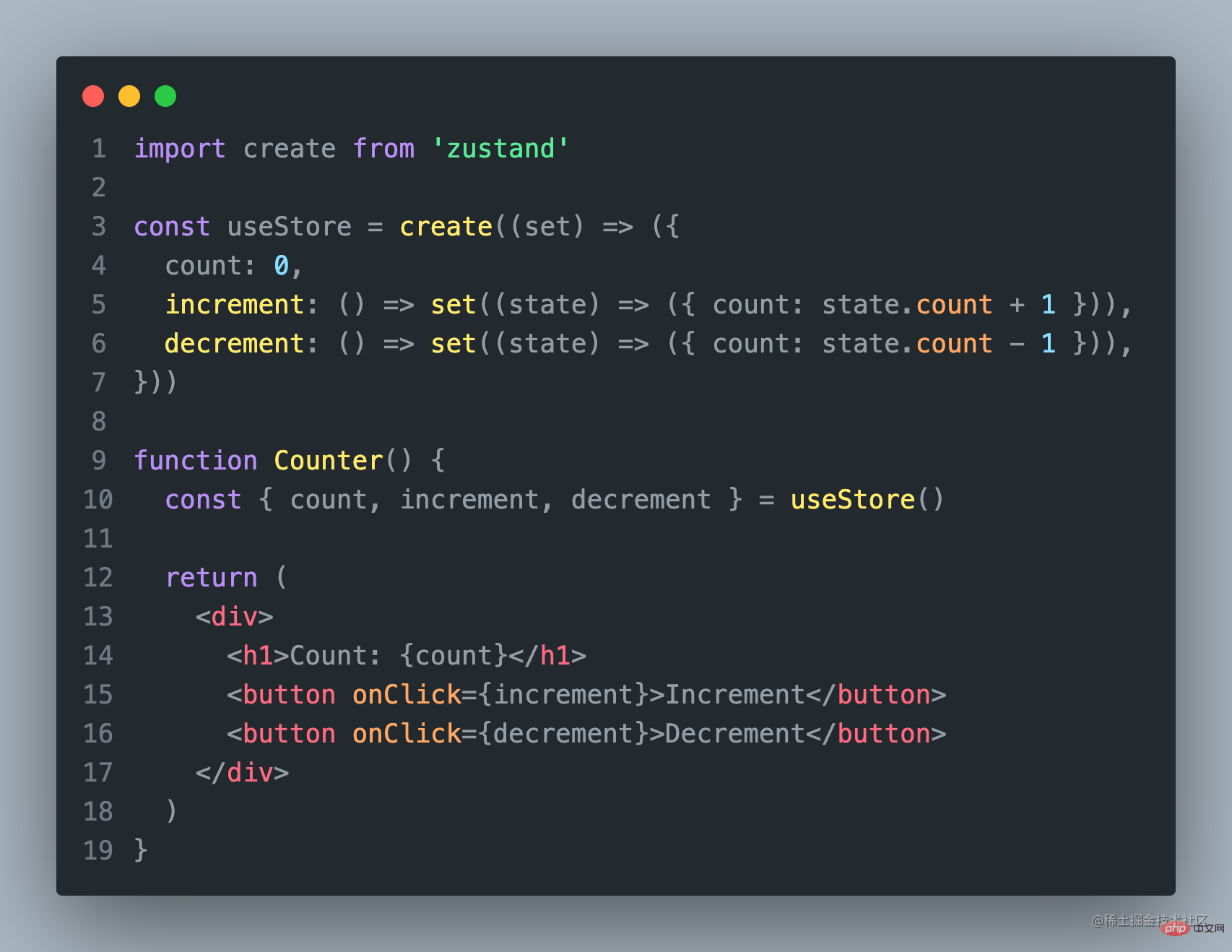
Zustand Code
使用Zustand,你可以将状态存储在一个单一的store中,并使用自定义的hooks来访问和更新状态。这使得状态管理变得非常简单和直观。
impo
.........................................................